Docker, Openvswitch & Aruba VXLAN Network Build
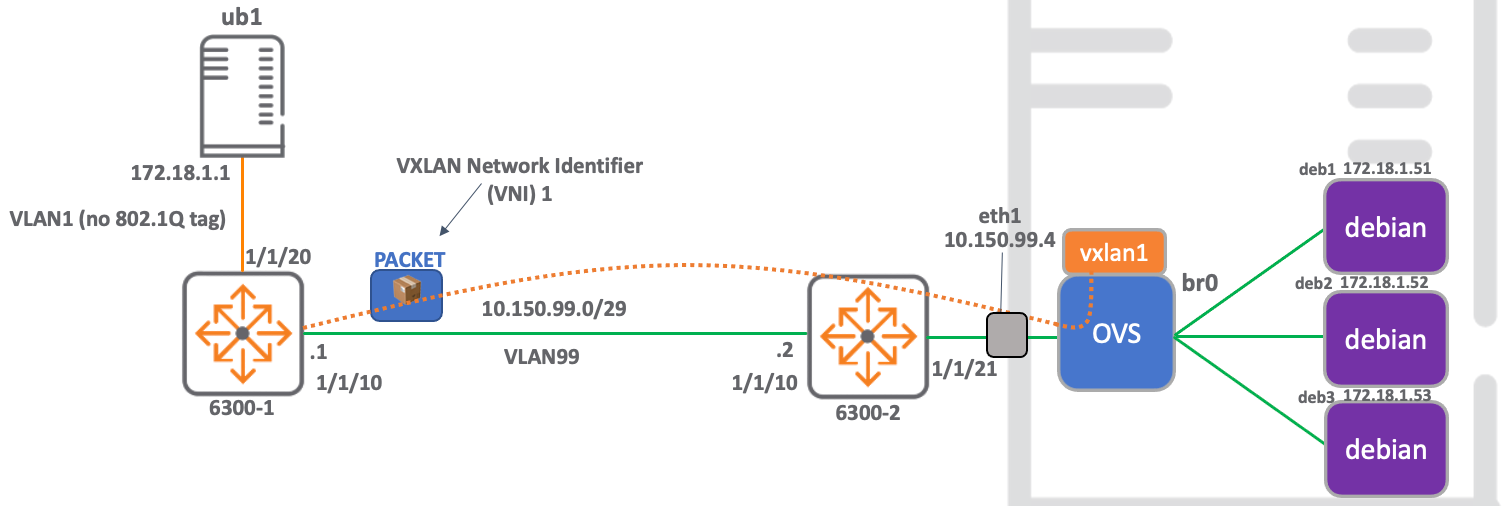
This blog provides details of how to build a static VXLAN network that connects physical hardware to a virtualised network, enabling communication from docker containers to external nodes.
The build is comprised of a hardware ArubaOS-Switch acting as a VTEP and an openvswitch VTEP running on an ubuntu server, which is the host for the docker containers.
This network also serves to prove interoperability between the ArubaOS-Switch VXLAN stack and that running on openvswitch.
The use of docker containers as target nodes enables rapid deploy and tear-down of network components, which is particularly useful in lab environments for testing.
Kit List
2 x ArubaOS-CX 6300 hardware switch (only 1 is required.)
1 x HP EliteDesk PC running Hyper-V hosting an ubuntu 21.04 VM
1 x HP EliteDesk PC running ubuntu 21.04 bare metal.
Notes:
I used a VM for the openvswitch / docker linux server to take advantage of snapshots while documenting this build. This server can be any linux server.
Network Diagram
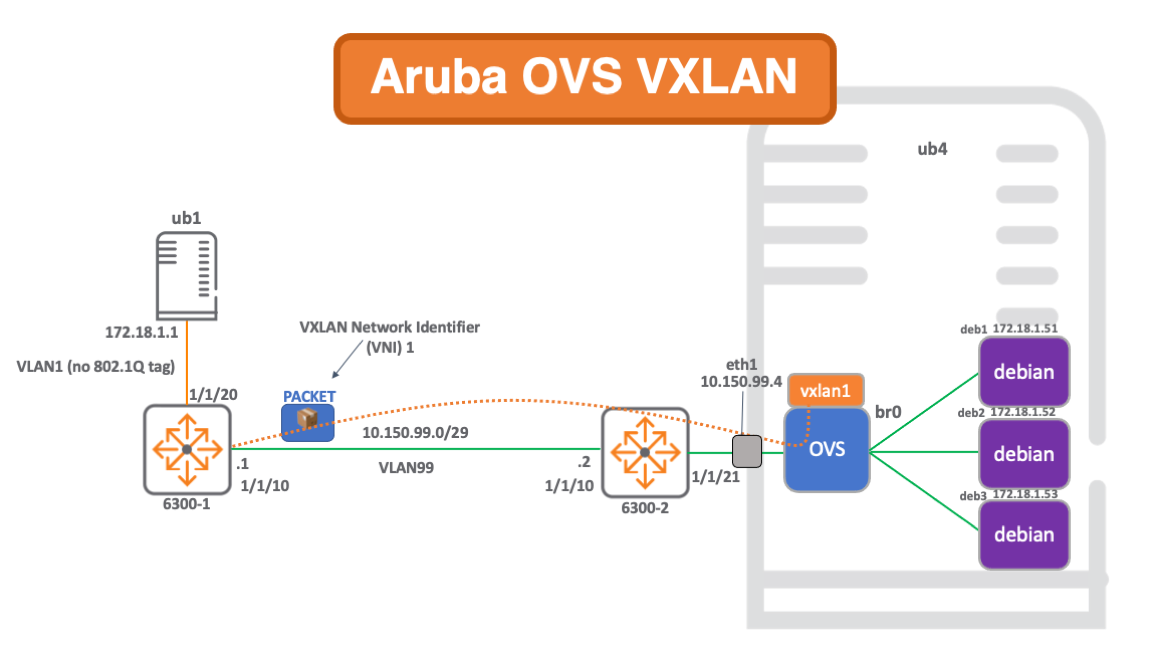
Build Steps
Configure the ArubaOS-CX hardware switch
- Configure the ArubaOS-CX switch and local server (172.18.1.1) so that they are in the same subnet and can ping each other.
- Configure the ArubaOS-CX switch and the remote server in a different subnet and ensure connectivity with a successful ping. This subnet will act as the underlay for the VXLAN traffic.
- Configure the ArubaOS-CX switch to act as a VTEP. This build uses static VXLAN, all destination VTEPs and VNIs must be manually configured.
Build the openvswitch docker host Linux Server
- Install docker, these steps were copying from the official docker installation docs here.
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
echo \
"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- Input docker post-installation steps.
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker joe
logout
- Install openvswitch.
sudo apt -y install openvswitch-switch
Configure the openvswitch docker environment
- Create an alpine docker container, this will act as the target server, with Layer 2 connectivity to external server 172.18.1.1 (ub1).
docker run -di --name al1 alpine
- Add a bridge to openvswitch.
sudo ovs-vsctl add-br br0
- Add a VXLAN port to the new openvswitch bridge, and configure a remote VTEP address and VNI to be assigned to that port.
sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 vxlan1 -- set interface vxlan1 type=vxlan options:remote_ip=10.150.99.1 options:key=1
- Use the ovs-docker tool to add a port connecting the docker container and ovs bridge.
sudo ovs-docker add-port br0 eth1 al1 --ipaddress=172.18.1.51/24
- Test with a ping.
docker exec al1 ping 172.18.1.1
- Clean up.
docker kill al1
docker rm al1
sudo ovs-docker del-port br0 ether deb1
sudo ovs-vsctl del-br b0
Note on container image
Originally I build the lab using a debian image, version 10.10.
However, debian has since rolled to 11.0 and this image does not contain ping nor iproute2.
This can be fixed by:
- Using the debian 10.10 image: debian:10.10
- Using debian 11 and adding the required packages to the image.
- Using an alpine image, as I have done here.
